When creating documents, there are a few steps that can be followed in order to make your content as accessible as possible.
Please keep in mind that these steps are for the creation of .docx files, not for .rtf files. .rtf files cannot be made accessible without removing all images, because alternate text cannot be added to images in .rtf files. Please keep this in mind when choosing your file format.
Using Check Accessibility Tool
Use the Check Accessibility tool to determine accessibility issues with your document and follow the prompts to fix issues. The Check Accessibility tool is located under File > Info > Check for Issues in Microsoft Word 2016 and under Review in Office 365. The tool will not report all inaccessible content, see the instructions below to manually correct common accessibility issues with documents and presentations.
Manually Making a Document Accessible
If not using the Check Accessibility Tool, use the following steps:
-
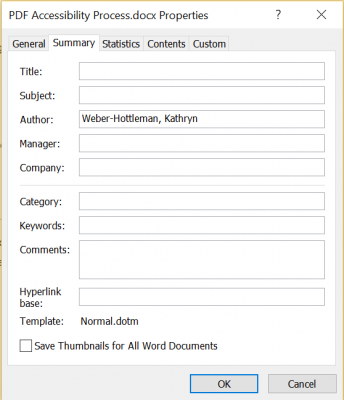
Under File, select Properties
- Click Advanced Properties
- Under Summary, add a Title property
- The Title must be descriptive of the document’s content; it may be the same as the filename
-
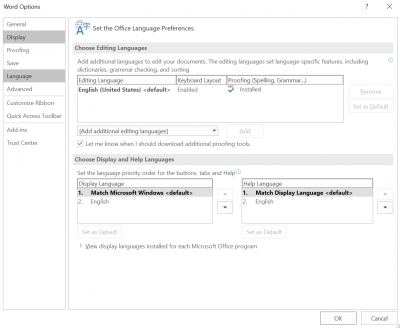
If your document is in a language other than English, select Review
- Under Language, choose Language Preferences
- Set the editing language and, if necessary, the display and help languages
-
Use predefined heading styles to create semantic structure instead of bold, italics, or underline to set apart headings (Heading 1, Heading 2, etc.)
- In your Word document, under Styles, select the heading level you would like your text to be. Typically, there is one Header 1; subsequent headers are Header 2, then Header 3, and so on.
- Use heading styles to determine heading levels for your document
- Rule of thumb for headings: Typically, the bigger and bolder the heading is, the higher the heading level
- Change the appearance of the heading style
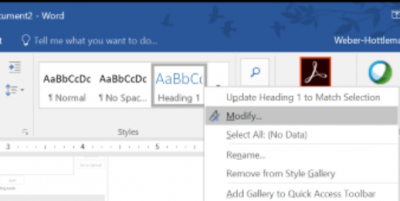
- Choose the heading style you would like to change
- Right click on the heading style
- Click on modify
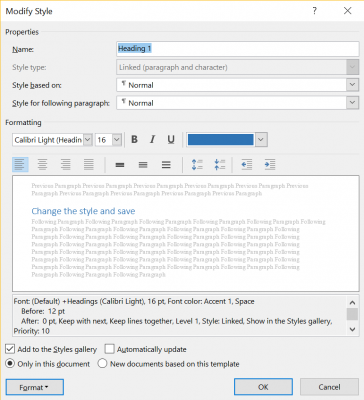
- Change the style and save
- Avoid hitting Enter or Return after a heading to create extra space after your heading
- Instead, highlight text after which you want the space
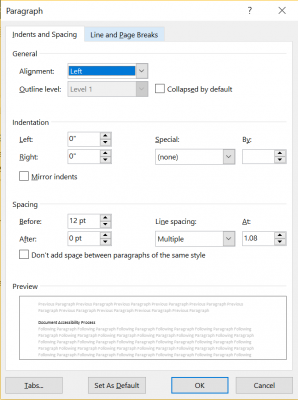
- Right click on the text
- Click Paragraph
- Increase the space after the paragraph
- Click Ok
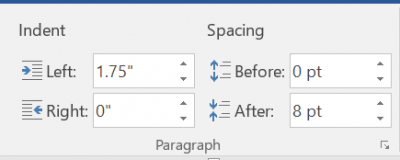
- Alternatively, highlight text after which you want the space
- Choose Layout
- In the Paragraph section, increase Spacing after the text
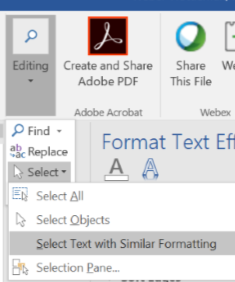
- To apply a heading style to all similarly styled text, click Select
- Choose Select all text with similar formatting
- Click on the desired heading
- Instead, highlight text after which you want the space
-
Set links in text as hyperlinks with meaningful link text
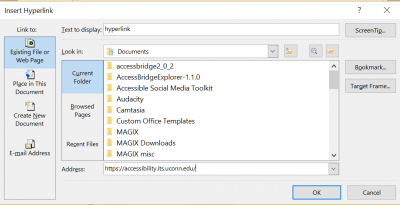
- Select text to be hyperlinked: Avoid “click here” and instead have text describe the link’s target
- Under Insert, select Links
- Click on Hyperlink
- Add the desired URL
-
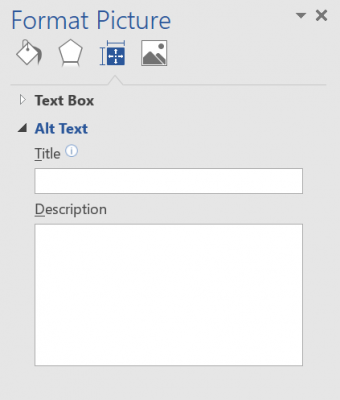
Set ALTs (alternate text) for all images
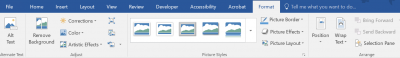
- Ensure that all of your image alignments are set to In line with text
- Click on any image in your document
- Under Format, click Alt Text
- Enter your alternate text for the image
-
Use an accessible font
- Fonts with serifs, like Times New Roman, can be difficult to read for people with low vision or learning disabilities
- Fonts like Arial and Calibri, sans serifs, are easier to read
- Use a font size of at least 12 pt.
-
Include transcripts or textual descriptions for all purely audio or purely visual media
-
Use only captioned multimedia
-
Check the document for color dependence
- Ask if the document uses color only to convey meaning
- Example of color dependence: "All red items are required"
- Example of no color dependence: "All red, bold items are required"
-
Check the document's color contrast using Color Contrast Analyser or Color Contrast Pal
- Contrast should meet a ratio of 4.5:1 (foreground: background colors)
- Adjust colors as necessary
-
Set table headers
- Click on the table
- Under Design, ensure that Header Row and/or First Column is checked
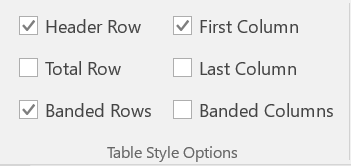
- Use Header Row if headings are over columns
- Use First Column if headings are by row
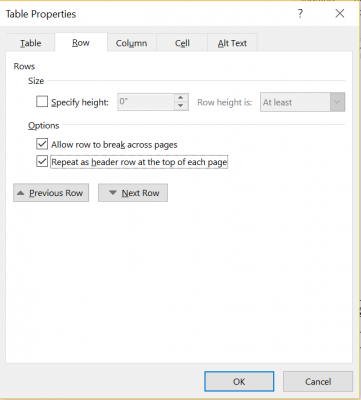
- Right click on the table
- Under Table Properties, check the box for Repeat as header row at the top of each page
- This ensures that the table will be accessible if the document is converted to a PDF
MS Word Forms
-
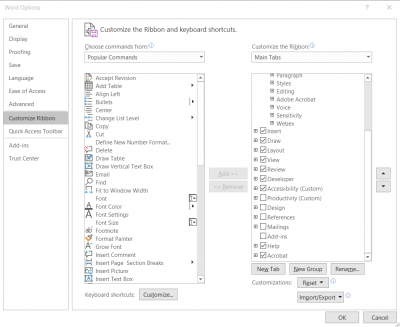
Add the Developer tab to the Word ribbon.
- Navigate to File > Options > Customize Ribbon
- Check the Developer checkbox
-
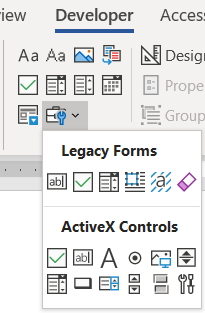
Add form elements.
- In the Developer tab, in the Controls panel, insert Legacy Form Fields from the drop down
- Examples of Legacy Form Fields include Text form field, Checkbox, and Drop-Down
- To add ActiveX Controls, enter Design Mode in the Controls panel and insert ActiveX Controls
- Examples of ActiveX Controls include Option buttons and Combo boxes
- In the Developer tab, in the Controls panel, insert Legacy Form Fields from the drop down
-
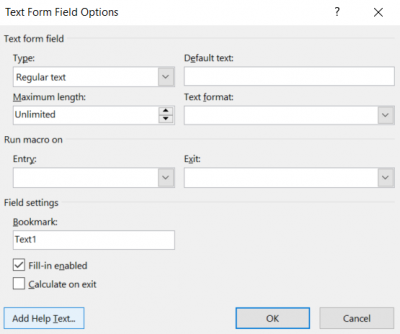
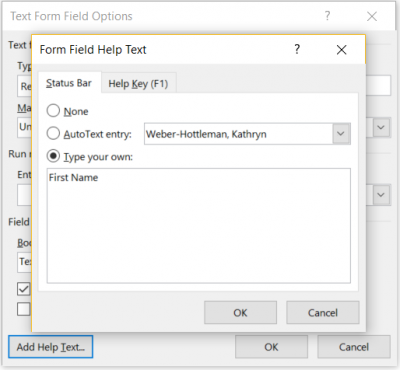
Add help text to Legacy form fields.
- Select the form field and select Properties OR right click on the field and select Properties
- Select the Add Help Text... button
- Under Help Key (F1), type help text into the textbox
- The help text might be the same as the form field's label; for example, if the field is for the respondent's first name, the help text might read "First Name". If the field asks for a user's experience, the help text might read "Give an example of your experience".
-
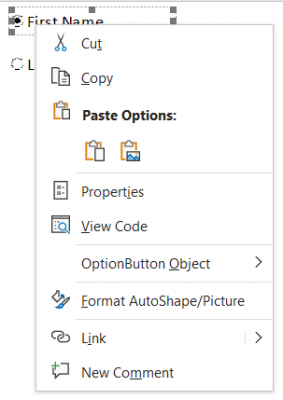
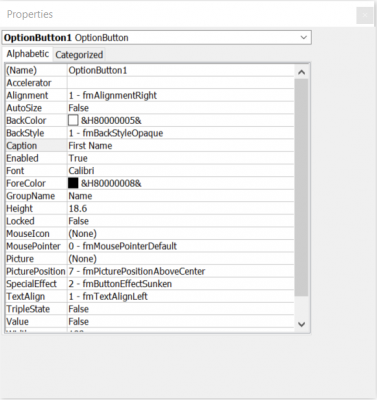
Add help text to ActiveX Controls
- Enter Design Mode under the Developer Tab, in the Controls pane
- Insert the ActiveX control into the page
- Select the form field and select Properties OR right click on the field and select Properties
- In the Properties panel, change the Caption and the Group Name
- The caption is what will display next to the ActiveX control
- The group name describes the objects that are grouped together. For example, fields for first and last name may have a group name of "Name". The group name prevents multiple options within the same group from being activated, so this is particularly useful for radio or option buttons
- Close the Properties panel
- Exit Design Mode to make the controls available to users
-
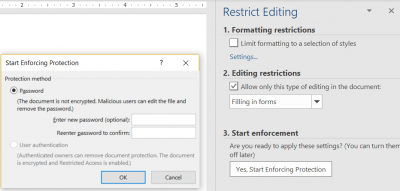
Restrict editing to make the form work with assistive technology, like screen readers
- On the Developer tab, select Restrict Editing
- Under Editing Restrictions, check the box next to Allow only this type of editing in the document:
- In the drop down, choose Filling in forms
- Activate the Yes, Start Enforcing Protection button
- Enter a password (optional)
Watch This Video on Document Accessibility
Last modified May 27, 2021