An accessible PowerPoint draws on techniques for creating accessible media, multimedia, and documents. Please visit the Documents and Media and Multimedia sections to learn more about creating accessible documents and media.
You can also use the Accessible PowerPoint Checklist while creating your PowerPoint. To learn more about accessible PowerPoints, go read this article from Microsoft. Microsoft also provides some accessible templates for PowerPoint to help you as you design presentations.
Using Check Accessibility Tool
Use the Check Accessibility tool to determine accessibility issues with your PowerPoint and follow the prompts to fix issues. The Check Accessibility tool is located under File > Info > Check for Issues in Microsoft PowerPoint 2016 and under Review in Office 365.
Manually Making PowerPoint Accessible
If not using the Check Accessibility Tool, use the following steps:
-
Use templates to set the slide’s correct reading order
- PowerPoint will already have an idea of logical reading order based on the objects in a predefined layout
- To adjust reading order: Under Home, click Arrange
- Click Selection Pane
- This will show you the slide’s tab order
- Note: PowerPoint tab order reads from bottom to top; this means that the first item read by a screen reader will be the bottom item in the selection pane
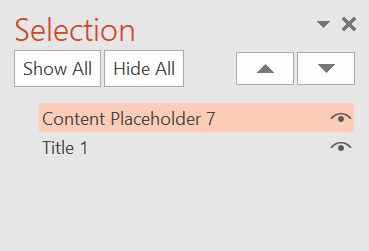
- In the above image, the first item read would be Title 1
-
To modify templates, go to View and click on Slide Master
- Slide Master allows you to edit template layouts
- Use the selection pane to see the layout’s tab order
- After modifying the layout, adjust the tab order to follow a logical reading order
-
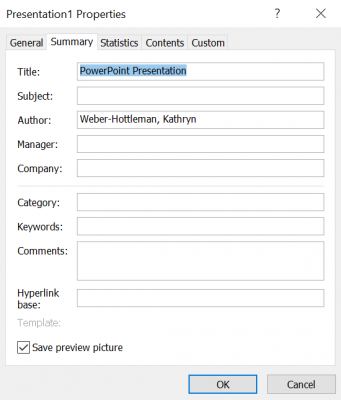
Under File, select Properties
- Click Advanced Properties
- Under Summary, add a Title property
- The Title must be descriptive of the document’s content; it may be the same as the filename
-
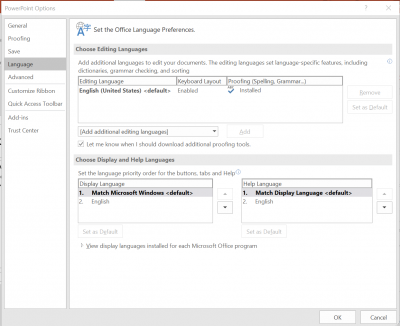
If your PowerPoint is in a language other than English, select Review
- Under Language, choose Language Preferences
- Set the editing language and, if necessary, the display and help languages
-
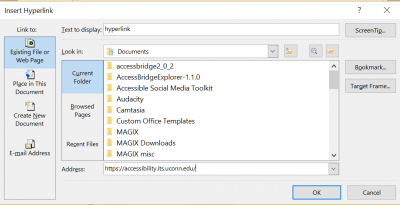
Set links in text as hyperlinks with meaningful link text
- Select text to be hyperlinked: Avoid “click here” and instead have text describe the link’s target
- Under Insert, select Links
- Click on Hyperlink
- Add the desired URL
-
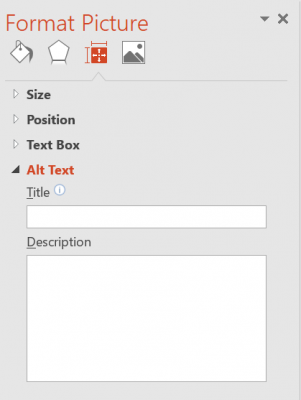
Set ALTs (alternate text) for all images
- Right click on any image in your document
- Click Format Picture
- Under the Size & Properties tab, choose Alt Text
- Enter your alternate text for the image
-
Set ALTs (alternate text) for all charts and graphs
- Click on a chart or graph
- Under Format, select Format Selection
- Under the Size & Properties tab, choose Alt Text
- Enter your alternate text for the chart or graph
-
Use an accessible font
- Fonts with serifs, like Times New Roman, can be difficult to read for people with low vision or learning disabilities
- Fonts like Arial and Calibri, sans serifs, are easier to read
- Use a font size of at least 11 pt.
-
Include transcripts or textual descriptions for all purely audio or purely visual media
-
Use only captioned multimedia
-
Check the document for color dependence
- Ask if the document uses color only to convey meaning
- Example of color dependence: "All red items are required"
- Example of no color dependence: "All red, bold items are required"
-
Check the document's color contrast using Color Contrast Analyser or Color Contrast Pal
- Contrast should meet a ratio of 4.5:1 (foreground: background colors)
- Adjust colors as necessary
- Put text on solid backgrounds
- Keeping text on solid backgrounds makes it easier to read for users who have vision impairments or learning disabilities
- It can also help keep attention on the text, which is valuable for those with attention difficulties
-
Minimize animations and eliminate flashing elements
- Some users have disabilities that can be triggered by moving or flashing material
- Simple animations and avoidance of flashing elements helps to make your slides usable for these individuals
-
Set table headers
- Click on the table
- Under Design, ensure that Header Row and/or First Column is checked
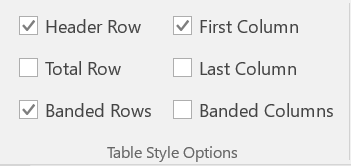
- Use Header Row if headings are over columns
- Use First Column if headings are by row
Watch This Video on PowerPoint Accessibility
Last modified February 26, 2019